
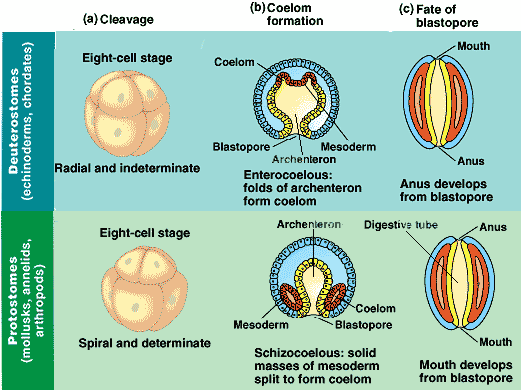
Protostome vs Deuterostome Embryo Development. molluscs, annelids, platyhelminths, and rotifers). arthropods, nematodes) and the Spiralia (e.g.
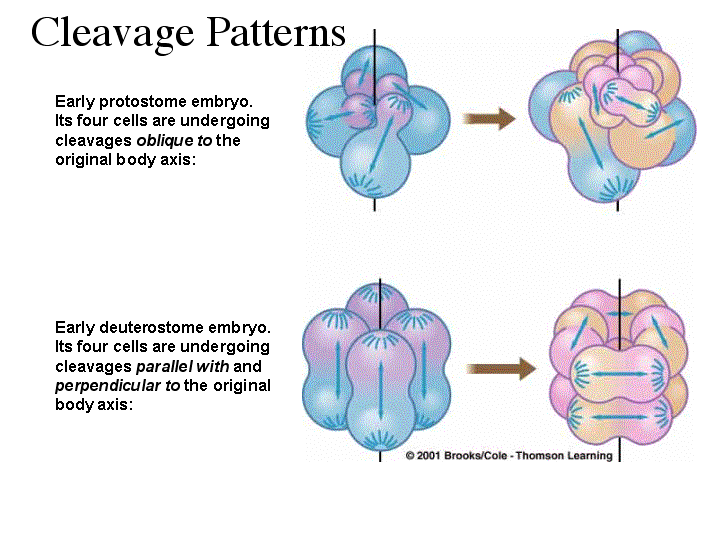
Together with the emerging results on the conservation of segmentation genes, these results reinforce the hypothesis that Urbilateria had a segmented trunk developing through posterior addition. Protostomes are divided into the Ecdysozoa (e.g. In addition, caudal and even-skipped are likely involved in the posterior addition of segments.

All three genes are shown to be likely involved in the building of the anteroposterior axis around the slit-like amphistomous blastopore as well as in the patterning of the terminal anus-bearing piece of the body (the pygidium). In an annelid, bra is expressed in the complete furrow indicating that this structure represents the blastopore. Annelids belong to the still poorly studied third large branch of the bilaterians, the lophotrochozoans, and have anatomic and developmental characteristics, such as a segmented body plan, indirect development through a microscopic ciliated larva, and building of the trunk through posterior addition, which are all hypothesized by some authors (including us) to be present already in Urbilateria, the last common ancestor of bilaterians. The Higher Animals - two lineages Higher animals have a coelom and a mouth/anus The infolded blastopore of the forming. In order to address the question of the conservation of posterior growth mechanisms in bilaterians, we have studied the expression patterns of the orthologues of the genes caudal, even-skipped, and brachyury in the annelid Platynereis dumerilii.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
